
| Blog | Tabs | Projects | About |

| Blog | Tabs | Projects | About |
A triad is formed by combining three notes of a scale:
This is a C-Major triad, excluding the notes F and D:
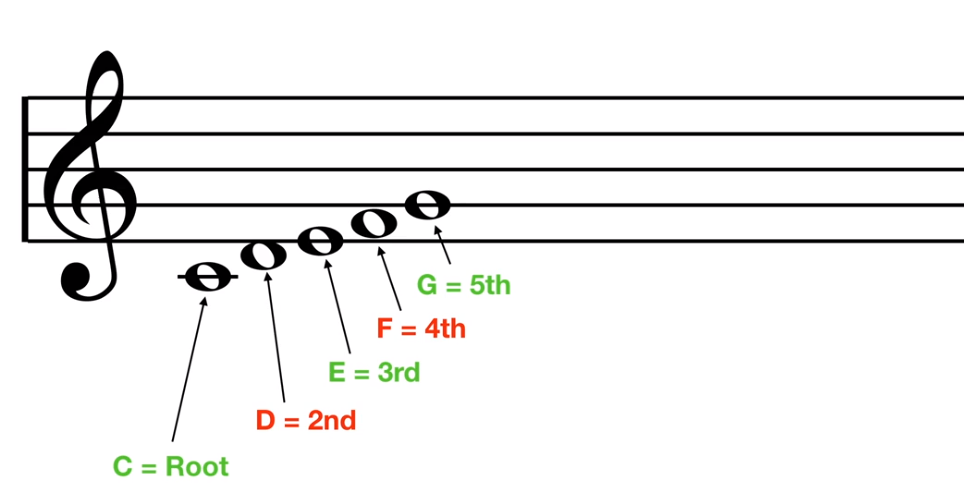
To change a chord from major to minor or vice-versa, you need to modify the 3rd note, i.e. the mediant. In minor chords, you just flatten the 3rd note of the scale.
For example, C-Major has the notes C, E and G. C-Minor, on the other hand, has the notes C, E♭ and G. A C Major chord is represented by the letter "C", whereas a C Minor chord is represented by "Cm".